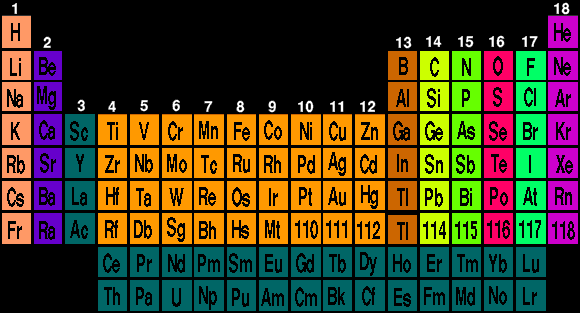
Select an element for description of element. [POP]
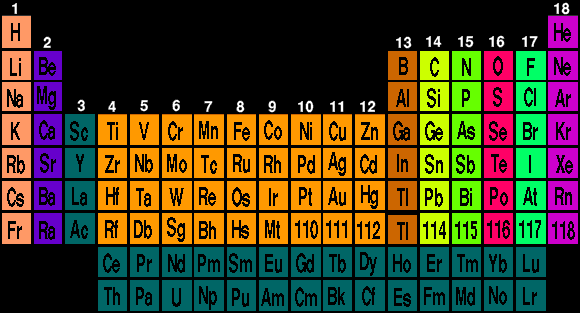
HELP on ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
The electrons in an atom are grouped in shells 1, 2, 3, 4, etc which are further divided into sub-shells, s, p, d, f, g, h, etc and can hold only certain numbers of electrons before they are full. Thus we have 1s; 2s, 2p; 3s, 3p, 3d; 4s, 4p, 4d, 4f; 5s, 5p, 5d, 5f, 5g; 6s, 6p, 6d, 6f, 6g, 6h; 7s, ... But this is not the order in which the shells fill, which is based on their energy levels. Orbits occupied by electrons are shown in yellow, orbits vacant are shown in blue. The electrons in outer shells and in unfilled shells are responsible for the properties and valences exhibited by that element.
HELP on VALENCES
The valency of an element, if negative, is the number of atoms of hydrogen (or its equivalent) which that element can hold in chemical combination, (or which it can displace ,if positive). The valency of an ion is equal to its charge. Valences range from -4 to +8. Those exhibiting valences above +4 are said to be hypervalent or 'octet expanded' because they do not obey the octet completion rule, examples being SF6 or OsO4.
Valences shown in green are preferred, those in orange commonly displayed, and those in red rarely exhibited.
![]()